Insight Recruitment: ENI's Expertise

Qualitative research and the UX overlap

ENI & Sue Phillips – Qualitative Research

Liz Norman & Anastasia Alexis – An international career in Insight

Liz Norman & Febronia Ruocco – Client-side, end user Insight roles

ENI & Caroline Bates – Why Insight over Research?
Insight produces strategic recommendations for business/govt/marketing based on an accurate and deep understanding of people and the markets they influence.
Part of the wider data, information and analytics profession, insight focuses on the analysis of purely people data and the markets they influence. How they behave, what they like, what they select, products/designs that work for them, how they can be influenced, etc.
Areas of Insight Recruitment ENI supports includes:
- Data Analysis,
- Innovation,
- Market Research,
- Market Intelligence,
- Research and Data Tech (Includes MarTech),
- CX/UX,
- Strategic Planning,
- Data Science,
- Category,
- Operations, Commercial.
You can browse through our videos, highlighting our ‘insight expertise’, and learn more about the ever-changing area with us, as it develops in the future.
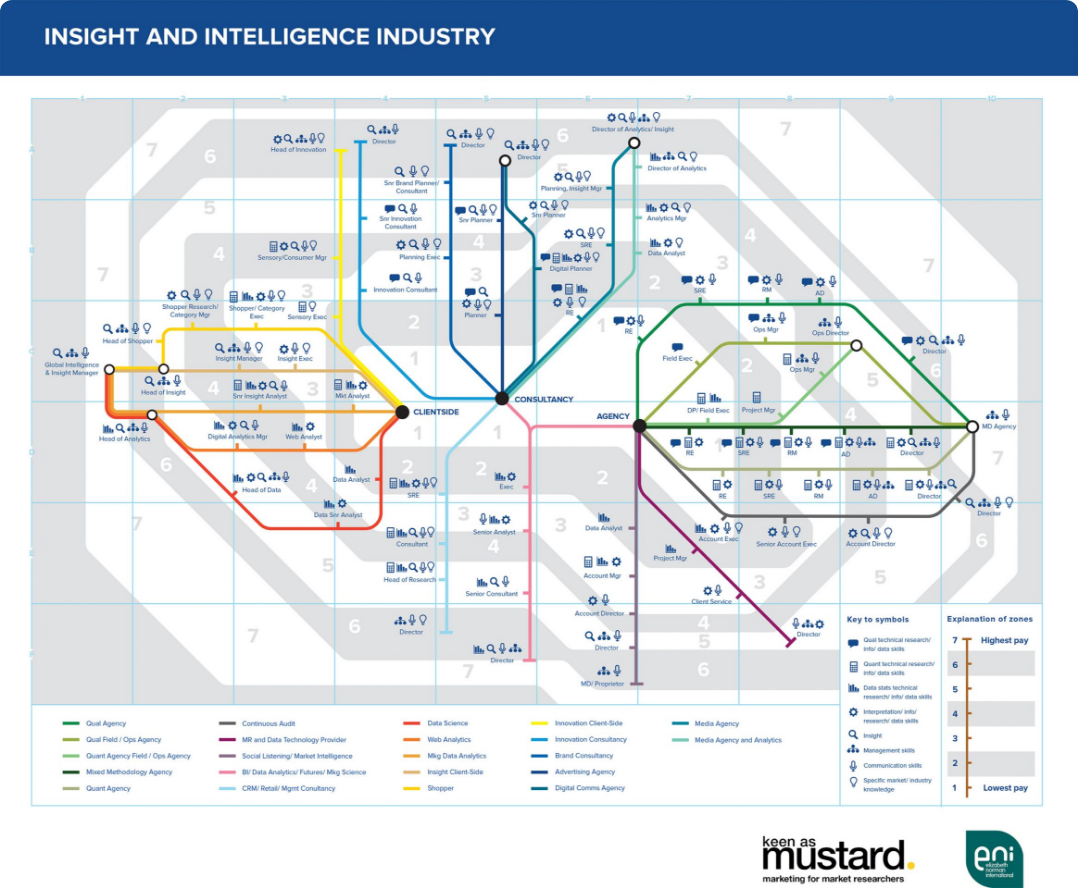
Insights Careers Map: View Our Infographic
In just the UK alone, the Insight sector is worth more than £7billion, employing more than 64,000 people. Complex and rapidly growing, it is at the heart of strategic planning across a wide range of organisations and markets. This has led to a need for a huge variety of skills and backgrounds, each with their own job title so it’s not an easy profession to navigate.
The below infographic shows the key employer areas of Insight.
- Client-side: represents organisations both large and small whose focus is on getting the right insight information to the right people, at the right time and in the right format to drive change.
- Consultancies: represents organisations who similarly use information to drive change, but change for their clients rather than themselves.
- Agencies: represents all the organisations related to the gathering and analysis of data, including disciplines such as market research, market and competitor intelligence and data analytics.
- Tech: represents organisations that provide the technology to make the gathering and analysis of the information possible.
The routes show the career paths within insight and some of the most common job titles. The zones reflect the salary bands those roles fall into, and the symbols reflect some of the most commonly sought skills.
Contact us or connect with us on LinkedIn for more information on roles in Insight.
Download InfographicFAQs
No, only recruiters who pay for a certain licence can see this. If you are open to hear opportunities, please turn it on, it helps us reach out to candidates who want to hear about new roles!
Data analysis is literally the analyzing of data. Data Analytics is broader and encompasses the collecting and organization of that data.
- Data Science
- Tech
- Customer User experience
- Qual
- End User/Clientside.
- Market Intelligence
Yes, although the term is used less commonly now and is often replaced by Strategist.
No! Market researchers were never the people who asked the questions. They are the people that design the research and analyse the results. People standing in the street asking questions are often the fieldworkers, but Insight tends not to gather data in this way anymore.
Planner, a job title coined in the 50’s and 60’s by advertising agencies who realised that understanding the deeper motivations and drivers of the consumer and adding that knowledge to the creative process, enabled them to develop more persuasive advertising. Today the title is still used by a broader range of organisations interested in understanding those deeper drivers and how they contribute to strategy beyond advertising strategy, and so ‘Strategist’ is sometimes used instead, particularly for more senior roles.
It’s hard to get into Data Science with out the relevant academic qualifications and programming skills. If this is the root you want to go (even if you are already working as a Data Analyst) we suggest looking at getting an appropriate qualification. A degree in statistics, maths, business administration or computer science is a viable option to pursue a career as a data scientist. If this isn’t an option, experience in the following will help: R programming, Python coding, Hadoop platform, SQL Database/coding, Apache Spark, Machine Learning and AI.
R is slightly more advanced and is something you can learn later in your career, so you don’t necessarily need to learn R to do Data Science.
AI helps synthesis huge amounts of qualitative or language based information, which would be impossible for individuals to do manually. For example, if assessing opinions discussed on social media over a particular issue, only with AI would it be possible to analyse everything discussed. In a world where we do everything digitally, AI is becoming more and more important.
Whilst there are some differences in reality there is a lot of overlap between the two definitions and many organisations can be described as both. Consultancies focus on providing advice rather than the collection and analysis of information, where as an agency will be more focused on the collection and analysis. However many business provide both services, so it’s never normally that clear cut!
Agencies tend to be smaller, with a team of experts in a specific field. An agency could work on planning, strategy, design, management, communication of a product or service. Business might work with several different agencies to meet their business needs because the specialised nature of agencies means that they come in to implement a particular thing or deliver a specific project.
Consultancies are similar in what they do but able to provide a higher level of cross discipline guidance. Consultancies tend to advice on long-term projects or strategies and are more likely to communicate exclusively with C-suite roles.
Consultancies build from the top downwards, and agencies build from the ground upwards. So while their services might look similar or overlapping, this perspective is key because it shapes how forge their partnerships and projects.
CX means customer experience. Broader than its roots in customer satisfaction, it covers everything the customer experiences, their interaction with the organisation (in terms of past-present perception, experience and future intentions) across every touchpoint and channel. CX drives growth and that’s why companies are focusing more and more on retaining customers and recovering those at risk.
Category is a marketing term. It refers to a group of related products, for example healthy snacks, shampoo or tinned dog food and how best to promote that broader product area. Interested in the overall product area rather than the individual brands within it, insight to support category is interested in trends and behaviour across the all the brands within that category, rather than individual brand preference/performance. Overall trends for the sales of shampoo for example. As a result category insight tends to be very data focused using a lot of retail audit/continuous and sales data.
Mystery shopping is a method used from “marketing” research to measure quality of service in stores, job performance, regulatory compliance or to gather information about competitors’ products and services. Mystery shoppers are not researchers, they are usually independent contractors who mirror customers to understand specifics on products and services; they submit detailed feedback reports about their experience.
B2C is the type of commerce where businesses sell products or services directly to consumers, by passing the normal retail outlet. B2B is the exchange of products, services or information between businesses, for example selling car batteries to car manufacturers.
On-line communities allow individuals with something in common to swap experiences and knowledge around that area of interest. By accessing that community it is possible to qualitative researchers/insight professionals to learn more at the area of interest by following what is being discussed or ask the community for it’s opinion on related subjects. It’s particularly useful when opinions are sought from niche and hard to find groups in society.
Available roles
Senior Fieldwork Executive
-
Permanent
-
£28,000
-
-
-
£30,000
Are you an organised and proactive Project Manager ready to take the lead on exciting projects? We are looking for an enthusiastic Project Manager or Junior Project Manager to join an innovative research agency with a supportive, solution-focused culture. Project Manager – Recruitment & Fieldwork Location: Leeds, 5 days in the office Salary: £28000 – £30000 You will work on exiting innovation and product testing projects, and be part of a collaborative team that values authenticity, partnership, and positivity. What you’ll do: Take ownership of projects, ensuring they run smoothly, accurately, and on time. Communicate clearly and proactively with clients, keeping them updated every step of the way. Spot and flag potential facility capacity issues with the Fieldwork Manager. Drive improvements and innovate the way we work. Manage project incentives, ensuring everything is accounted for ahead of time. Create quotes and lead facility hire projects. About you: You may have experience as a Project Manager, Fieldwork Coordinator, or similar. You bring confidence in leading people or small teams. You have a process-led mindset, love structure, systems, and processes. You can spot problems and quickly find smart, creative solutions. You have strong written and verbal communication skills. Curiosity about people, behaviour, or research. Experience in market research fieldwork is a bonus but not essential. This is a great opportunity for someone open minded with a passion for understanding consumer and product interaction! 🔸 Please apply for next steps. We encourage applications from individuals of all backgrounds and actively seek to embrace diversity across age, gender identity, sexual orientation, disability, race, religion, and sex. For successful applicants, a recruitment consultant will be in touch via email to schedule a briefing call. We will explain the role in more detail and share the company details before creating a formal application. Note: Due to the high volume of applications we receive, only shortlisted candidates will be contacted. Error: No job reference detected!
Quantitative Research Executive
-
Permanent
-
£30,000
-
-
-
£32,000
We’re on the lookout for a Research Executive with a strong foundation in quantitative research and a keen eye for what makes consumers tick. This is a fantastic step-up role for someone ready to grow in a fast-paced, insights-led environment. Quantitative Research Executive role London – Hybrid Salary up to £32k + bonus What you’ll be doing: Running hands-on quantitative research projects from start to finish Managing surveys, analysing data, and translating insights into actionable recommendations Supporting senior researchers on key client accounts Working across a variety of sectors Presenting findings clearly to both internal and external stakeholders What you’ll need: 1–2 years’ experience in a research or insight role Solid grasp of quantitative methodologies and tools Ability to turn data into compelling stories Strong organisational skills and a collaborative mindset Perks: Hybrid working Career development support and hands-on training Exposure to exciting projects with big-name brands Please apply for next steps. We encourage applications from individuals of all backgrounds and actively seek to embrace diversity across age, gender identity, sexual orientation, disability, race, religion, and sex. Error: No job reference detected!